Human life is inextricably tied to food consumption and intake, providing our bodies with essential sustenance for optimal function. Of the many foods we eat, sugar frequently makes an appearance in many diets and tempts us with its sweet taste; yet many remain skeptical if their bodies could survive without its sweet touch?
In this carefully crafted expose, we shall explore the complicated and dizzying world of sugar and its effects on our ailing bodily systems. We shall explain and illuminate a vital question: Can our anatomy survive without frequent doses of sugar? Additionally, we shall assess glucose's role in overall health while ascertaining its various identities within physiology.
Differing between natural and refined sugars, we will explore their detrimental effects and impacts on our bodies, thus uncovering their elusive nature and unmasking any secrets they hide from us.
As part of our discussion, we will navigate the complex relationship between carbohydrates and energy. Our discussion will dissect all the details and intricacies of low glycemic index foods to understand their impacts on energy levels, along with providing helpful strategies on incorporating them into diets successfully and seamlessly.
As we embark on this voyage of discovery, we shall immerse ourselves in the fascinating and complex world of sugar and its relationship to brain function. We shall explore how sugar infiltrates cognitive ability and impairs cerebral faculties without our knowledge, while offering prescriptive tips for maintaining healthy brain function without succumbing to excessive sugar consumption.
As we read through this opus, one burning question will occupy our thoughts: Can our bodies live without sugar? Prepare yourself for an exciting voyage of discovery ahead.
I. Glucose Production
Consumption of carbohydrates begins a complex conversion process in our bodies that converts them to glucose - the simplest form of sugar - essential for our daily survival. While glucose may provide energy directly into cells for proper functioning, many may wonder whether our body could survive without resorting to any sugar at all - contrary to popular belief our bodies do produce glucose naturally, yet for optimal functioning it must still be included as part of a balanced diet for maximum effectiveness.
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis - our bodies' spontaneous production of glucose - occurs naturally within our livers and kidneys and plays an integral part of maintaining adequate levels of glucose within our bodies. Carbs are the primary energy source our bodies require; as such, an adequate consumption of carbohydrates must be achieved in order to provide enough glucose to cells - otherwise our bodies will begin breaking down other sources such as protein into glucose in an inefficient manner, leading to muscle depletion as well as other negative health impacts.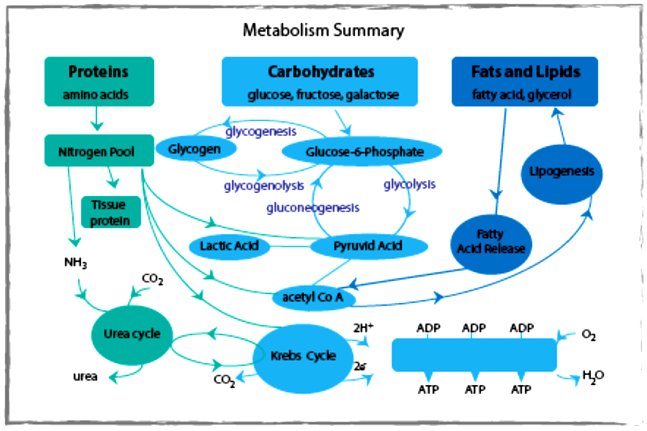
Importance of Glucose for Survival
A person needs glucose for survival depending on factors like their age, weight, activity level and overall health. Our brains depend on glucose for proper function while our muscles depend on it for movement. Guidelines for glucose intake will differ for everyone; it is crucial, however, to highlight that maintaining a balanced diet is integral for optimal body functioning. So while it is technically feasible to live without sugar, eating enough carbohydrates to ensure the body receives sufficient glucose is recommended. An individual may gain many advantages by cutting back or eliminating refined sugar from their diet, but to remain healthy overall a balanced approach should also be maintained.
Conclusion
In conclusion, glucose is crucial for our body's survival and optimal functioning. While our bodies can produce glucose naturally, it is still important to consume a balanced diet that includes an adequate amount of carbohydrates. By doing so, we can keep our bodies healthy and functioning at their best.
II. Natural vs Refined Sugars
Deciphering natural and refined sugars is key when discussing sugar. Natural sugars are found in fruits, vegetables, and grains while refined ones tend to reside in confectionary products and soft drinks that may contribute to weight gain or diabetes. While consuming natural sugars can have beneficial health effects on their own, excessive consumption of refined ones could have detrimental health repercussions.
Consequences of Refined Sugar Consumption
As one of these consequences, inflammation seems to play a prominent role. A diet high in refined sugars may wreak havoc on our bodies by unleashing a systemic inflammatory response and increasing our likelihood of contracting various diseases. Furthermore, excessive consumption can contribute to obesity, insulin resistance, and high blood pressure - three conditions associated with refined sugar consumption.
Minimizing the Health Consequences
To lessen and minimize the unwanted health consequences caused by refined sugars, one effective strategy would be to scrutinize food labels. While seemingly healthy items, like granola and yogurts, can contain significant levels of added sugars; in order to decrease consumption of processed food and increase consumption of fruits and vegetables which would abate inflammation response and promote overall wellness.
Replacement options could also include natural sweeteners such as honey or maple syrup; while still contain sugar, these natural alternatives tend to be less processed and provide more beneficial nutrients compared to their refined counterparts.
Conclusion
Reducing refined sugar consumption can have numerous health advantages. One may switch to natural sweeteners or whole foods as alternatives to promote better health and diminish systemic inflammation response, thus decreasing any negative consequences arising from an excessive consumption of refined sugars.
Learn more at brevardhealth.org about Natural vs Refined Sugars.III. Carbohydrates and Energy
As we explore nutrition, carbohydrates are undeniably vital in powering our bodies' fundamental functions. But not all carbs are created equal: certain high glycemic index carbohydrates quickly convert to glucose for instant energy boosts followed by crushing drops resulting in an energy drain causing fatigue and exhaustion.
Therefore, replacing high glycemic index carbohydrates with lower glycemic index ones to prevent this unpleasant event would make sense. Carbs such as whole grain products, fruits and vegetables offer excellent alternatives as their digestion allows for a steady release of glucose throughout the day and also contain essential vitamins and nutrients that are so necessary to proper body functioning.
Fiber-Rich Foods Slow Carbohydrate Digestion
Imagine being able to slow carb digestion by including fiber-rich foods into your diet. Whole grains, vegetables like broccoli, kale and spinach as well as fruits such as apples, berries and oranges all contain low glycemic index carbohydrates as well as being fiber-rich options are excellent ways of doing just this.
Consume more low glycemic index foods and you will experience noticeable physical benefits in terms of energy levels and general well-being. Your body will appreciate receiving optimal nourishment through balanced, whole food nutrition.
Opt for Low GI Foods for Optimal Health
Opting for foods with low glycemic index ratings can help maintain energy levels and benefit your health in numerous ways. Whole grains, fruits and vegetables all contain essential life-giving nutrients - their presence should not be taken for granted!
Learn about Carbohydrates and Energy at Harvard School of Public Health.IV. Brain Function and Sugar
Sugar and brain function have an intimate connection. Gluconate is an energy source used by the brain, with low levels causing fatigue, confusion and concentration difficulties when consumed at too high a dose. Conversely, excessive consumption can have detrimental impacts on cognitive ability.
Effects of Refined Sugar Consumption
Refined sugar consumption causes a temporary rise in blood sugar levels, creating feelings of hyperactivity. Unfortunately, however, this temporary surge leads to rapid drop-off of glucose and subsequent fatigue and debilitation for many of its consumers. This cycle can create acute levels of stress on brain capabilities as a whole.
Healthy Alternatives
Experts advise consuming natural sources of sugar such as fruit or honey instead of processed food to maintain optimal brain function without an increase in sugar consumption. By doing this, your brain will receive its necessary supply of glucose while at the same time improving overall health.
Add healthy fats, such as avocados and nuts, into your diet regularly in order to promote cognitive function. Not only should these healthy fats fuel your mind with fuel for cognitive function; staying hydrated throughout the day is just as crucial - dehydration levels have a direct correlation to cognitive impairment, making it harder for you to stay focused and complete tasks effectively. Staying hydrated requires regularly drinking water throughout the day so as to maintain proper cognitive health.
Conclusion
Overall, our brains rely heavily on glucose for proper functioning, making sugar an integral component. Unfortunately, though, excessive consumption of refined sugars may have detrimental effects on cognitive abilities. Focusing more on whole food diet and incorporating healthy fats like olive oil and staying hydrated are excellent strategies for maintaining proper cognitive function and well-being and healthy cognitive performance.
Conclusion:
Living without sugar may seem daunting at first. We know glucose is essential to optimal body functioning, prompting one to consider what it would mean to consume only natural sugars found in whole food rather than refined ones. Research indicates that cutting back on refined sugar intake has numerous potential advantages including reduced inflammation in the body, mitigated risks associated with obesity and insulin resistance as well as enhanced cognitive capabilities - sounds impressive doesn't it?
However, you can take even further steps towards improving brain function by prioritizing low glycemic index foods and including healthy fats in their diet - providing a steady source of energy throughout the day. While our bodies could survive without sugar in moderation, consuming too much can have harmful health consequences; hence baby steps towards adopting a lifestyle without sugar can eventually create healthier outcomes for you!