Are you trying to live a healthy, sustainable vegan life? If that is the case for you, essential fatty acids - specifically omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids - play an integral part in supporting many functions essential to survival, from cognitive performance to quelling inflammation and improving heart health. Be mindful when selecting essential fatty acid sources.
Olive oil stands out as one of the key components in plant-based diets due to its versatility and welfare benefits, but there still seems to be confusion regarding its contribution towards omega-3 and omega-6 intake. Olive oil may provide us with important fatty acids; in this abstract we shall dismantle this myth and uncover all its nutritional advantages. As part of our expedition, we'll also discover herbal alternatives for omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids as well as olive oil's anti-inflammatory qualities - providing some astounding facts that may compel you to include olive oil as part of your daily dietary regime! Our journey will unveil some surprising facts that may make you want to add olive oil into your daily regiment!
I. Olive Oil - An Omega-3 or Omega-6 Source?
As we explore the fascinating world of essential fatty acids, one of the first questions we encounter is whether olive oil can provide sufficient amounts of omega-3 or omega-6 essential fatty acids. Both play an integral part in maintaining optimal human health; without an appropriate balance of both types, we increase our risk for inflammation and growth disruptions.
Essential and Non-Essential Fatty Acids
So where does olive oil stand among this spectrum of essential fatty acids? First let's understand what constitutes essential and non-essential fatty acids: omega-3s and omega-6s are both considered essential since our bodies cannot produce them on their own; such sources as flaxseeds, chia seeds and walnuts provide omega-3s, while vegetable oils containing sunflower, safflower, corn and soybean oils often provide omega-6s as essential fatty acids. Meanwhile non-essential fats like monounsaturated fats provide nutritional value but are not essential as essential fatty acids are not synthesized by our bodies to create Omega-6s and vice versa. 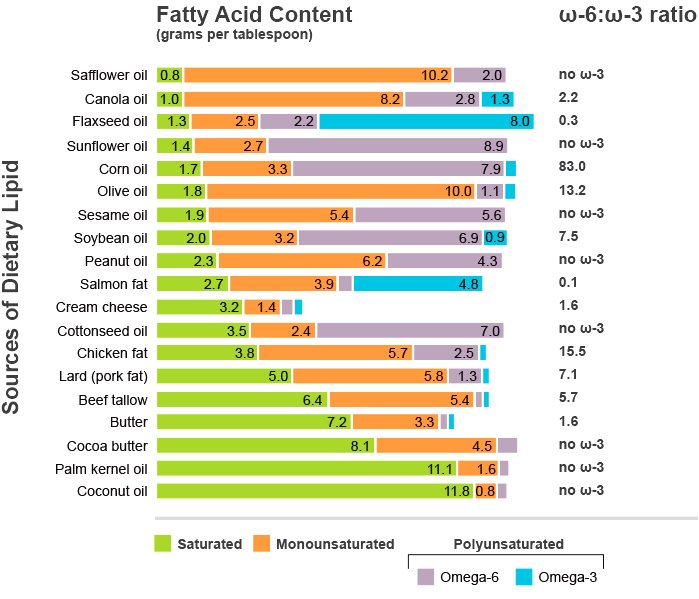
Olive Oil's Omega Fatty Acid Supplements
But what about olive oil? From Mediterranean regions to Middle Eastern cuisines, olive oil has quickly become a household name worldwide. Extracted from the fruit of an olive tree, this highly popular oil has long been recognized for its health-giving benefits such as cholesterol reduction and heart health promotion; yet many question whether it provides adequate omega fatty acid supplements. Although olive oil does contain trace amounts of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), this quantity does not qualify it as a reliable source.
The Advantages of Olive Oil
Olive oil offers several distinct advantages over other oils like sunflower and soybean oils in terms of omega-6 content. While too much omega-6 can lead to inflammation and other severe health conditions, under-consuming omega-6s or over-consuming omega-3s can equally cause problems; thus it is crucial that we maintain an ideal ratio of these fatty acids in our diets.
Olive oil may not provide us with omega-3 or omega-6 fatty acids; however, it is an excellent source of monounsaturated fats and other essential nutrients that offer numerous health benefits. Understanding its nutritional profile allows us to make informed decisions and promote overall wellbeing.
Learn more at Olive Oil Source.II. Olive Oil - An Omega-3 or Omega-6 Source?
Olive oil has long been revered for its exquisite taste and versatile applications in gourmet kitchens, and this delicious oil makes an exceptional addition to any balanced diet. As one of its main components is monounsaturated fat, which gives olive oil its characteristic rich and distinct taste, its popularity cannot be denied.
Monounsaturated Fats and Health
Monounsaturated fats offer many health advantages, from supporting heart health and inhibiting inflammation to increasing insulin sensitivity and supporting cell membrane health and skin health. Furthermore, these essential fats play a key role in creating healthier cell membranes and mitigating risks of type 2 diabetes.
Olive oil stands out as the leader among oils when it comes to its high concentration of monounsaturated fats, known as monounsatured fatty acids, or MUFs, for consumption in reasonable amounts. Studies have revealed these MUFs can significantly decrease LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, decreasing risk for heart disease. Furthermore, their inclusion may contribute to decreasing risk for cancer and other illnesses.
Virgin and Extra-Virgin Olive Oil
Virgin and extra-virgin olive oils contain higher concentrations of monounsaturated fatty acids, nutrients, and antioxidants than others types. Furthermore, virgin and extra-virgin olive oils are extracted without using heat or chemicals, providing purer oil with more pleasing flavor that contains phenolic compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that provide greater flavor profile and improved taste experience.
Essential Nutrients in Olive Oil
Olive oil provides essential nutrients that support healthy living, yet only contains trace amounts of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Consuming it moderately, as its calories and fat intake is high; typically one or two tablespoons daily is enough for most individuals.
Vegetarian Sources of Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Following, we will delve into vegetarian sources of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids and offer advice for including them in your vegan diet.
>"Olive oil is an excellent addition to any balanced diet, providing numerous health benefits and a delicious taste. However, it is important to consume it moderately, as it is high in calories and fat. Opting for virgin or extra-virgin olive oil provides additional health benefits and a purer, more delicious flavor."
Include Olive Oil in Your Balanced Diet for Optimal Health
Adding a moderate amount of olive oil, particularly virgin or extra-virgin olive oil, to your daily diet is an excellent way to support heart health, inhibit inflammation, and enjoy a tasty addition to your meals. By incorporating a variety of other vegetarian sources of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, you can further support a healthy and balanced lifestyle.
Learn more at chriskresser.com.III. Monounsaturated Fats in Olive Oil
Although olive oil is known for its health benefits, it should be noted that it doesn't pack as many omega-3 and omega-6 essential fatty acids. Don't despair though; many plant-based foods offer ample sources of these essential fatty acids - making it simple and straightforward for vegans to incorporate them into their diets.
Plant-based Omega-3 Sources
Flaxseed, chia seeds, hemp seeds and walnuts are some of the most sought-after plant-based omega-3 sources. From smoothies to salads or muffins - flaxseed can fit seamlessly into any diet plan and please even picky tastebuds! Additionally, increasing omega-3 intake through these sources is crucial in staving off cardiovascular illnesses - thus making them essential components of our daily lives.
Linoleic Acid - Omega-6 Fatty Acid
Linoleic acid, an essential omega-6 fatty acid, can be found in nuts and seeds such as almonds, sunflower seeds and pumpkin seeds as well as vegetable oils such as safflower, sunflower and corn oil. Omega-6s play an integral part of diets; however, to prevent inflammation, it is vital that there be an equilibrium between omega-3 and omega-6s in one's daily routine.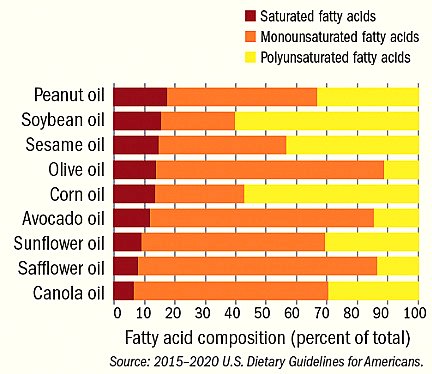
Not all sources are equal
However, it's important to keep in mind that not all sources of these essential fatty acids offer equal nutritional profiles. Chia seeds offer excellent omega-3 fatty acid sources but may be higher in calories for those looking to gain or maintain weight. Algae-derived omega-3 supplements could be more suitable as vegan and vegetarian sources of these essential fatty acids.
>Integrating plant-based sources of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids into one's diet is a must for leading a balanced and healthful life. Even though olive oil only has negligible omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acid content, it would be wrong to disregard its powerful anti-inflammatory properties; we will discuss more in our following discussion section.
IV. Plant-Based Sources of Omega-3 and Omega-6
Olive oil has long been valued for its many beneficial qualities; yet its pathophysiological mechanisms remain shrouded in mystery. Inflammation is a natural biological response triggered by your immune system to defend against various infections or injuries to protect itself against harm. But prolonged inflammation can result in serious health conditions like malignant cancer, pernicious diabetes and coronary artery disease - among others. Pertinently, omega-3 fatty acids have long been linked with anti-inflammatory effects while omega-6s are widely known to trigger pro-inflammatory processes. Achieve a delicate balance between these two species is thus necessary in controlling inflammation.
Olive oil offers an extraordinary array of attributes, boasting anti-inflammatory benefits that may reduce chronic disease risks. A number of bioactive compounds contribute to this property; none more so than phenolic compounds which contribute bitter taste in virgin and extra-virgin olive oils as well as many health advantages.
Numerous carefully researched studies reveal that olive oil's phenolic compounds possess both anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can effectively curtail inflammation while protecting from oxidative stress. Furthermore, olive oil consumption may reduce risk factors related to arthritis, cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes while possibly helping lower hypertensive patients' blood pressure; consumption of high quality extra-virgin olive oil is therefore key in order to achieve adequate amounts of phenolic compounds needed for these benefits.
Olive oil presents many impressive health advantages. But overconsumption may prove harmful and should be limited. One can incorporate olive oil by sprinkling it onto salads or adding it when sautéing vegetables.
Olive oil is an invaluable culinary treasure and essential component in a vegan diet, and should never be considered an extravagance. Thanks to its nutrition profile and numerous health benefits, olive oil stands as an indispensable asset with unique anti-inflammatory compounds providing optimal health support.
Conclusion
Olive oil offers numerous health benefits. There are various varieties of olive oil available on the market, such as extra-virgin, virgin and refined varieties ranging in taste, color and processing method. Furthermore, its distinct aroma and flavor enhance meals to make them more appetizing and enjoyable to consume.
Olive oil can bring many health advantages to vegan diets. While not a major source of omega-3 or omega-6 fatty acids, olive oil contains essential vitamins and nutrients that promote good health due to its monounsaturated fat content as well as various phenolic compounds with anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties to provide overall well-being benefits. However, moderation should always be practiced when it comes to olive oil consumption in order to avoid unnecessary fat and calories which could potentially lead to weight gain.
To reap the maximum health benefits from olive oil, it's recommended to consume between one and two tablespoons daily, which should provide optimal health advantages. You have various varieties available such as extra-virgin, virgin, and refined oils so you can select one suited to your preferences and culinary needs. Integrating olive oil into daily meals adds richness and depth that can delight the senses!




